One of the most important and widely used metrics to measure the effectiveness of a digital marketing campaign is CTR, or Click-Through Rate. Whether you’re running a pay-per-click (PPC) campaign, sending email newsletters, or managing a social media ad, CTR gives you valuable insight into how well your content is engaging your audience.
In this article, we’ll dive into what CTR is, how it’s calculated, why it matters, and ways to improve it.
1. What is CTR (Click-Through Rate)?
CTR stands for Click-Through Rate, which is a metric used to gauge the percentage of people who click on a link compared to the total number of people who view the link, ad, or email. It essentially measures how effective your ad, content, or email is in compelling users to take action by clicking through to another destination, such as a website, landing page, or product.
Formula for CTR:
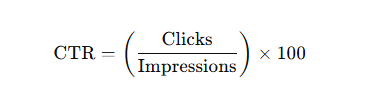
Here:
- Clicks: The number of times a link, ad, or call-to-action (CTA) was clicked by users.
- Impressions: The total number of times the link or ad was seen by users.
For example, if your ad received 1,000 impressions and 100 clicks, your CTR would be:
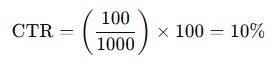
2. Why is CTR Important?
CTR is important because it provides insight into how engaging and relevant your ads or content are to your audience. A higher CTR indicates that users are finding your content appealing and are more inclined to interact with it. Here’s why CTR matters:
- Measure of Engagement: CTR shows how successful your content is in capturing user attention. If people are clicking, it means your ad or content resonated with them.
- Indicator of Relevance: High CTRs often mean that your ad or content is relevant to your target audience. This can be especially important in search engine advertising (e.g., Google Ads), where relevance plays a major role in ad rankings and costs.
- Quality Score in PPC: In platforms like Google Ads, CTR is a key component of your Quality Score, which affects your ad rankings and cost-per-click (CPC). Ads with higher CTRs tend to have better Quality Scores, which can reduce the cost of advertising.
- Conversion Funnel Insight: CTR is a good early indicator of how well your marketing funnel is working. It helps you assess whether users are moving from the awareness stage to the consideration stage by clicking through your ads, emails, or links.
3. What is a Good CTR?
What constitutes a “good” CTR varies depending on the industry, platform, and type of campaign. However, as a general rule of thumb, a CTR between 2% and 5% is often considered strong for many campaigns. In some industries, you might see CTRs as high as 10% or more, while in others, even a 1% CTR might be considered excellent.
To better understand what’s a good CTR for your specific campaign, consider factors such as:
- Industry: Different industries have different benchmarks. For example, a niche industry with limited competition might have a higher average CTR than a competitive industry.
- Platform: CTRs can vary depending on whether the campaign is run on Google Ads, social media platforms, or email marketing.
- Ad Type: Display ads generally have lower CTRs than search ads because search ads are shown to users who are actively looking for information. Display ads, on the other hand, are more passive and shown to users while they browse websites.
4. Factors That Affect CTR
Several factors influence your CTR, and optimizing these factors can significantly boost your results:
- Ad Copy or Headline: The most critical part of any ad or link is the headline. A compelling, attention-grabbing headline or ad copy is crucial for encouraging clicks. The headline must match the user’s search intent or needs to be effective.
- Visuals: In visual platforms like Facebook or Instagram, the image or video is a major element that affects CTR. Clear, engaging, and eye-catching visuals can greatly increase the chances of a user clicking on your ad.
- Call to Action (CTA): Your CTA should clearly tell users what to do next (e.g., “Learn More,” “Shop Now,” or “Sign Up Today”). A strong, well-positioned CTA helps guide users toward taking action.
- Targeting: Reaching the right audience is essential. Ads that are targeted to users who are more likely to be interested in your products or services will generate higher CTRs. Poor targeting can lead to lower CTRs, as the ad is less relevant to the audience.
- Ad Position: In search engine marketing, the position of your ad on the search results page affects CTR. Ads that appear at the top of the page tend to receive more clicks than those that appear at the bottom.
- Relevance: Ads that closely match the user’s intent or interests tend to perform better. This is why it’s important to focus on keyword relevance in search ads and user segmentation in social media ads.
5. How to Improve CTR
Boosting your CTR involves optimizing several aspects of your campaigns. Here are some proven strategies:
- Refine Your Ad Copy: Focus on creating compelling headlines and ad copy that speak to your audience’s pain points, needs, or desires. Use persuasive language, highlight benefits, and create a sense of urgency where appropriate.
- Optimize Your CTA: Make sure your call-to-action is clear, strong, and aligned with the user’s intent. A well-placed and compelling CTA can drive more clicks.
- Use Targeted Keywords: For search ads, use keywords that are closely related to the search intent of your audience. Conduct keyword research to ensure that you’re bidding on relevant terms that match what users are looking for.
- A/B Test Ads: A/B testing allows you to test different variations of your ads to see which version performs better. You can test headlines, copy, CTAs, images, and ad formats to optimize your CTR.
- Segment Your Audience: In social media and email marketing, segmenting your audience by demographics, interests, or behaviors can improve CTR. Targeting smaller, more specific groups with personalized messaging often yields better results.
- Improve Ad Placement: For PPC ads, bidding strategies can affect your ad’s position on the search engine results page (SERP). Higher-ranked ads typically receive more clicks, so consider optimizing your bidding strategy to improve your ad’s placement.
- Enhance Visuals: If you’re running display ads or social media campaigns, ensure your visuals are high-quality and relevant to your target audience. Use bright, bold images or videos that capture attention.
6. Analyzing and Interpreting CTR
While CTR is an important metric, it’s crucial to interpret it in the context of your overall goals. A high CTR is a good sign that your ad or content is attracting attention, but it doesn’t always mean success if users are not converting after clicking.
- Combine CTR with Conversion Rate: A high CTR paired with a low conversion rate could indicate that while your ad is compelling, your landing page may need optimization. Conversely, a lower CTR with a high conversion rate may suggest that only highly motivated users are clicking.
- Use CTR to Adjust Bids: In PPC campaigns, CTR can help you determine which keywords or ad groups are performing well. Ads with low CTRs may require adjustment in bid strategy, ad copy, or targeting to improve performance.
7. Tools to Track CTR
There are several platforms and tools you can use to track and analyze your CTR, including:
- Google Analytics: Useful for tracking CTRs for various links, campaigns, and ads.
- Google Ads: Provides detailed reporting on CTR for paid search ads and helps optimize campaigns for better performance.
- Social Media Ads Manager: Platforms like Facebook Ads Manager and LinkedIn Campaign Manager offer CTR insights for social media ads.
Conclusion
CTR is a crucial metric in digital marketing that helps you measure the effectiveness of your ads, emails, and web content. It not only indicates how well your content resonates with your audience but also impacts the success of your marketing campaigns. By understanding how CTR works, what factors affect it, and how to optimize it, you can improve the performance of your campaigns and ultimately drive better results for your business.
Regularly monitoring and improving your CTR through A/B testing, keyword optimization, and targeted messaging will help you create more engaging, higher-performing marketing efforts.
Ready to have a custom plan made for your moving business to get leads coming straight to you? Click here to reach out for more information.

Leave a Reply